Picture this: A high-tech vault in a spy movie, unlocked by a fingerprint or iris scan. It’s sleek, secure, and efficient—everything a business owner dreams of when safeguarding sensitive data and critical systems. This is no longer fiction; it’s the new reality in securing modern enterprises.
For decades, businesses have relied on passwords to protect their operations. But with data breaches costing companies millions each year and stolen credentials responsible for 61% of all breaches, traditional methods are proving unreliable and costly.
Enter biometric authentication, a cutting-edge solution designed to meet the demands of modern businesses. At its core, biometrics uses unique physical or behavioural traits—like fingerprints, facial features, or even voice patterns—to verify identity. For companies, this means stronger security, streamlined processes, and improved customer trust.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a technology that uses biological data to verify identity, ensuring that only authorised individuals gain access to systems or services. It replaces outdated methods that rely on what you know (passwords) or have (cards or tokens) with who you are, providing an unmatched level of security and convenience.
Governments and corporations are leading the charge in adopting this technology, integrating biometrics into everything from fraud prevention to customer onboarding. The benefits are clear: reduced operational inefficiencies, decreased fraud losses, and enhanced user experiences—all critical drivers of business success.
Why Businesses Need to Pay Attention
As cybercrime costs skyrocket—projected to hit $10.5 trillion globally by 2025—businesses face mounting pressure to protect sensitive data while maintaining seamless operations. Biometric authentication offers a dual advantage: it enhances security and simplifies the user experience, reducing costly risks while boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
For businesses striving to gain a competitive edge in today’s digital landscape, biometric authentication isn’t just a "nice-to-have"—it’s a necessity. So, what makes this technology the gold standard for modern security? Let’s explore how it works and why it’s transforming industries around the world.
How Biometric Authentication Works
Biometric authentication is a sophisticated process that uses your body’s unique traits—like fingerprints, facial features, or iris patterns—to verify identity. Essentially, your body becomes your password, ensuring access is tied directly to who you are, not what you know or carry.
The Mechanics of Biometric Authentication
- Data Capture
The process begins when a biometric system captures a physical or behavioural characteristic. For example:- A fingerprint scanner records the unique ridge patterns on your finger.
- A facial recognition system uses a camera to map facial geometry, like the distance between your eyes or the shape of your jawline.
- Iris scanners analyse the intricate patterns in the coloured part of your eye.
- Data Conversion
Once captured, this raw biometric data is converted into a digital template using specialised algorithms. These templates are designed to extract only the essential data points required for comparison while discarding unnecessary information to protect user privacy. - Matching Process
The system compares the newly captured data to a stored template in a database or on the user’s device. If the patterns align within a predetermined threshold, access is granted; otherwise, it is denied. - Continuous Learning
Modern systems, powered by AI and machine learning, adapt over time. For instance, they account for changes like ageing or environmental factors, ensuring consistent accuracy. They also detect fraud attempts, such as deepfakes or spoofing using photos or masks.
Devices and Infrastructure
Biometric authentication works with a range of devices, from specialised hardware like fingerprint scanners and iris cameras to everyday tools like webcams and smartphones. These systems are often powered by cloud-based or on-premises software capable of handling large-scale data comparisons in real time.
Types of Biometric Authentication
As businesses strive to enhance security while delivering seamless user experiences, understanding the various types of biometric authentication is crucial. Each method offers unique advantages, and the choice often depends on the specific needs of your organisation. Let’s explore the most commonly used biometric technologies:
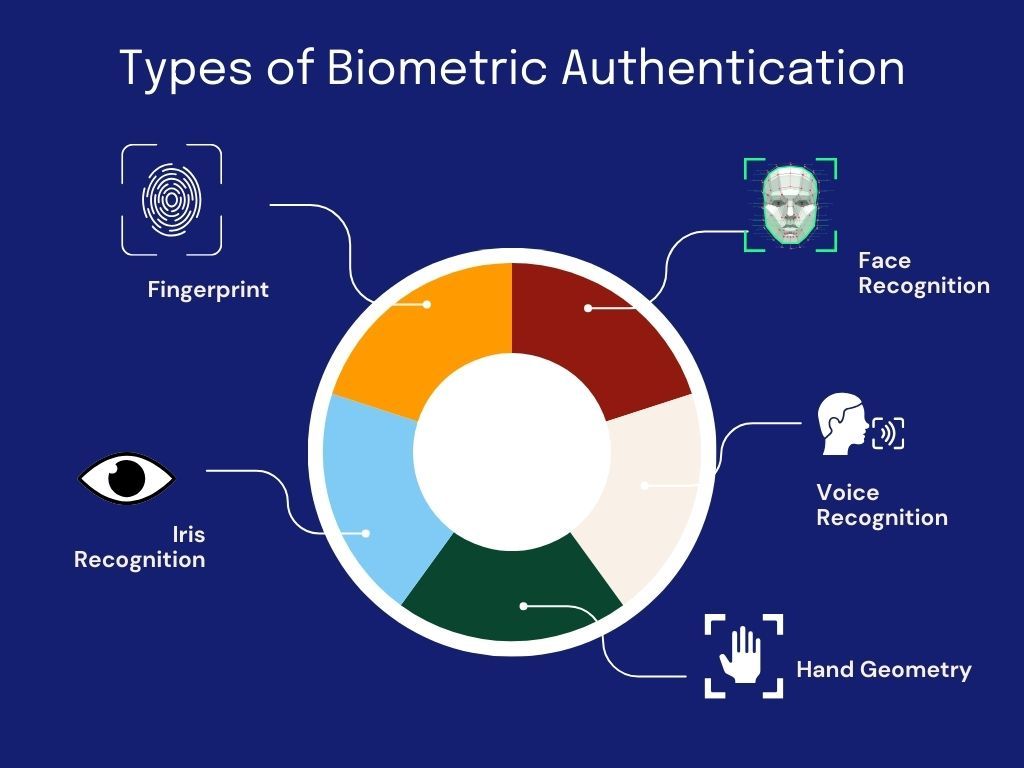
Fingerprint recognition remains a cornerstone of biometric security. Leveraging unique ridge patterns on an individual’s fingertips is highly accurate and nearly impossible to replicate. Businesses in high-security industries such as banking and healthcare rely on fingerprint authentication for its precision and ease of implementation. However, scalability and accuracy in certain environments remain challenging.
Often referred to as one of the most secure biometric methods, iris recognition scans the intricate patterns in the coloured part of the eye. It is highly resistant to spoofing and suitable for environments requiring heightened security, such as government facilities and research labs. However, its higher implementation cost might make it less attractive for smaller enterprises.
Facial recognition has become an industry favourite due to its non-intrusive nature. Advanced algorithms map facial features and compare them to stored templates, making it a go-to for fintech platforms in Africa like Smile ID’s SmartSelfie™ Authentication. This method is ideal for businesses focusing on fast, user-friendly authentication processes, such as digital onboarding in e-commerce and financial services.
Voice biometrics analyse vocal patterns to verify identity, often used in call centres and remote banking services. While convenient and easy to use, it can be susceptible to environmental noise interference, making it most effective in controlled environments.
5. Hand Geometry
This method measures the shape, size, and dimensions of an individual’s hand. Though less common than other forms, hand geometry is gaining traction in access control systems for physical locations like office buildings and secure data centres.
By understanding the types of biometric authentication available, businesses can strategically choose solutions that align with their operational goals and security needs. Whether opting for fingerprint scanners for their reliability or facial recognition for their versatility, biometric technology is redefining how organisations protect identities and data.
The Core Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Businesses increasingly adopt biometric authentication due to its numerous advantages over traditional methods like passwords or physical IDs. Here are the primary benefits:
1. Enhanced Security
Biometric data is nearly impossible to duplicate, making it a powerful defence against identity theft and fraud. Unlike passwords, which can be stolen or guessed, biometrics such as fingerprints or facial features are uniquely tied to an individual. Advanced systems like Smile ID’s liveness detection further bolster security by preventing spoofing attempts.
2. Improved User Experience
Forget the frustration of forgotten passwords or reset requests. Biometric authentication streamlines logins, payments, and access control, offering a seamless experience for users. This ease is particularly valuable in sectors like e-commerce, where smoother interactions directly impact customer satisfaction and retention.
3. Operational Efficiency
Automated biometric verification reduces manual checks, enabling faster onboarding and fraud detection. For example, financial institutions can verify users in minutes using biometric Know Your Customer (KYC) solutions, saving both time and resources.
4. Cost Savings
By cutting down on password management and fraud recovery costs, businesses can achieve significant financial benefits. Moreover, implementing biometrics eliminates the need for extensive physical security infrastructure, making it a cost-effective solution for scalable growth.
5. Scalability and Adaptability
Biometric systems adapt seamlessly to increased user volumes without compromising performance. As businesses grow, biometrics can scale alongside, ensuring consistent security and efficiency.
6. Future-Proofing
With biometric features remaining stable over a person’s lifetime, companies avoid the need for frequent system overhauls, ensuring long-term usability and ROI.
Potential Risks of Biometric Authentication
Despite its benefits, biometric authentication is not without challenges. Being aware of these risks allows you to make informed decisions and implement appropriate safeguards:
1. Data Breaches and Irreversibility
Unlike passwords, biometric data cannot be changed once compromised. If stolen, this unique identifier remains permanently at risk, potentially leading to long-term identity theft concerns.
Watchthe Webinar: Startup Security: Your Guide to Fraud Prevention.
Even the most advanced biometric systems can occasionally fail. False positives (unauthorised access granted) and false negatives (access denied to legitimate users) can disrupt operations or compromise security.
Some systems can be fooled by sophisticated forgeries, such as silicone fingerprints or 3D-printed facial replicas. However, cutting-edge technologies like Smile ID’s deepfake detection mitigate these risks by identifying fraudulent attempts in real-time.
4. Privacy Concerns and User Resistance
Some individuals may hesitate to share their biometric data due to privacy concerns or cultural preferences. Building trust through transparency and robust data protection measures is crucial for encouraging adoption.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Biometric data collection and use are subject to stringent legal frameworks. Non-compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, Africa’s POPIA) can lead to legal penalties and reputational damage.
6. Physical Changes
Ageing, injuries, or surgeries can alter biometric features like fingerprints or facial structures, potentially leading to authentication difficulties. Businesses must ensure their systems are robust enough to handle such variations.
Addressing the Challenges
To fully leverage the benefits of biometric authentication while minimizing risks, businesses should:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) combining biometrics with secondary verification methods.
- Partner with providers like Smile ID, who offer advanced fraud prevention features such as liveness detection, deepfake recognition, and compliance with global data protection standards.
- Regularly update your systems to stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure compatibility with changing biometric features.
Biometric Authentication and Data Security
Biometric authentication plays a critical role in modern identity verification, but concerns about data security and privacy are growing. In Africa, countries are progressively adopting regulations to address these issues, although frameworks are not yet uniform across the continent.
- South Africa: The Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) is South Africa's primary data protection law. It governs the processing of personal data, including biometrics, requiring businesses to obtain consent and implement stringent safeguards against misuse.
- Nigeria: Nigeria's Data Protection Regulation (NDPR) emphasises protecting personal data and mandates organisations handling sensitive data, like biometrics, to maintain high-security standards and ensure transparency in their usage.
- Kenya: The Data Protection Act of 2019 in Kenya aligns with global standards like GDPR. It specifies requirements for collecting, storing, and using personal data, including biometric identifiers.
Navigating the complexities of compliance can be challenging, especially with varying legal frameworks. Smile ID aligns its biometric solutions with global standards like the EU’s GDPR and incorporates safeguards to ensure data privacy and security.
In regions without comprehensive biometric laws, adopting global standards ensures proactive compliance, helping your business stay ahead as regulations evolve.
You must prioritise data privacy to avoid reputational risks and fines while demonstrating leadership in ethical technology adoption.
Biometric Authentication Use Cases
Biometric authentication isn’t a niche technology—it’s everywhere. Biometric authentication is revolutionising security across industries with its versatility and reliability. Here are some of its most impactful applications:
1. Identity Verification and KYC Compliance
Biometric technology simplifies and enhances Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance processes. Financial institutions can instantly verify customers during onboarding or transactions, ensuring accuracy and preventing fraud. This reduces reliance on manual document checks while meeting regulatory standards.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
By integrating biometrics with traditional security measures, MFA provides enhanced protection. For example, combining a password (something the user knows), a smartphone (something the user has), and a biometric scan (something the user is) creates a robust defence against unauthorised access.
Industries like banking, payments, and cryptocurrency exchanges leverage biometrics to stop account takeover attempts. Since biometric traits are unique, fraudsters cannot impersonate users even if they gain access to passwords or devices.
4. Fraud Prevention in Promotional Offers
Gaming, streaming, and delivery services often combat promo abuse, where individuals create multiple accounts to exploit new user discounts. Biometric checks match new account data with existing profiles, ensuring that offers are reserved for legitimate first-time users.
5. Mitigating Multi-Accounting
Peer-to-peer platforms, e-commerce sites, and educational platforms face challenges from users creating multiple accounts. For instance, students share accounts to avoid subscription fees or gamers using multi-accounting to gain unfair advantages. Biometrics help enforce one-user-per-account policies effectively.
6. Securing Physical Access
Biometric systems control access to buildings, secure areas, and restricted locations. Industries like logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare use fingerprint, facial recognition, or iris scanning to replace traditional key cards and PINs, improving security and convenience.
The Future of Biometrics in Everyday Life.
Related Reading: Biometric Verification - Complete Guide for User Verification
Biometric Authentication and Deepfakes: A New Era of Fraud
The rise of deepfake technology has introduced a critical challenge to biometric authentication. Deepfakes—highly realistic, AI-generated media—pose a significant threat to systems that rely on physical characteristics for identity verification.
Deepfake technology, originating from the combination of “deep learning” and “fake,” initially emerged as a tool for entertainment and creative purposes. However, its malicious applications have quickly escalated. Fraudsters now use deepfakes to bypass biometric systems by mimicking facial features, voices, and other identifiers with startling accuracy. In 2024, several reports have emerged accounting for deepfakes for over 40% of all biometric fraud cases, with financial services being the most targeted sector.
Biometric authentication offers advanced security, but combating deepfakes requires robust and layered defences:
- Liveness Detection: Advanced AI models detect subtle cues like micro-movements or changes in light reflection on the skin to verify that the biometric input originates from a live individual, not manipulated media.
- Behavioral Biometrics: By analysing patterns such as typing speed, device handling, or navigation behaviour, systems can detect anomalies indicative of fraud attempts.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Combining biometrics with additional verification layers (e.g., one-time passwords) significantly reduces the risk of successful deepfake attacks.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
The same AI advancements driving deepfakes are also pivotal in their detection. AI-powered fraud detection tools analyse the underlying inconsistencies in media files, such as pixel anomalies, unnatural movements, or mismatched audio-visual elements, to identify deepfake content.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
Businesses must adopt comprehensive strategies to mitigate the risk of deepfakes:
- Invest in Advanced Biometric Systems: Partnering with solutions like Smile ID ensures access to cutting-edge liveness detection and fraud prevention technologies.
- Education and Awareness: Training staff and customers to recognise deepfake threats is critical to reducing vulnerability.
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensuring compliance with data protection laws like GDPR, POPIA, or NDPR helps maintain trust while upholding security standards.
Wrapping Up
In an era where digital interactions dominate and threats like deepfakes loom large, biometric authentication is not just an option but a necessity. It stands at the intersection of security, user experience, and innovation, offering businesses a robust way to build trust, safeguard users, and stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated fraud tactics.
At Smile ID, we understand that protecting your users means more than keeping pace with threats—it means staying ahead of them. Our Biometric Authentication Suite is designed to empower businesses with cutting-edge technology tailored to the unique challenges of African markets.
Why Smile ID’s Biometric Authentication?
- Unmatched Accuracy: With our proprietary SmartSelfie™ technology, Smile ID achieves a 99.8% face-matching accuracy rate, thanks to machine learning algorithms trained on over 5 million African faces.
- Real-Time Liveness Detection: Protect against spoofing attempts and deepfakes by ensuring that every selfie is captured in real time by the user. Liveness detection ensures photos are of a live individual, safeguarding against even advanced fraud techniques.
- Fraud Prevention at Every Step: From account registration to high-value transactions, our solution offers seamless biometric two-factor authentication. By eliminating reliance on vulnerable SMS passcodes, we reduce risks of account compromises and enhance user convenience.
- Built for Africa, Built for Trust: By prioritizing inclusivity and regional specificity, our solutions adapt to local needs while maintaining global standards of excellence.
Ready to Secure Your Business?
Deepfakes and AI-driven fraud are reshaping the tech ecosystem, but your business doesn’t have to face these challenges alone. With Smile ID, you’re not just investing in technology—you’re partnering with a team dedicated to creating a safer, fraud-free future for businesses and users alike.
Start here - Explore the future of secure authentication with Smile ID.



